Set Root Password Mysql Mac
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL CREATE USER statement to create a new user in the database server.
- Set Root Password Mysql Macro
- Set Root Password Mysql Mac Command
- Set Root Password Mysql Mac Os
- Set Root Password Mysql Macros
MySQL CREATE USER syntax
The CREATE USER statement creates a new user in the database server.
Here is the basic syntax of the CREATE USER statement:
- Open the command-line mysql client on the server using the root account. Then you will want to run the following two commands, to see what the root user host is set to already: use mysql; select host, user from user; Here’s an example of the output on my database, which is pretty much the default settings.
- After you have set up a remote MySQL connection, you can use a MySQL client application to manage your databases. For more information, please see this article. Method #1: Set up an SSH tunnel. The procedure you follow to set up an SSH tunnel between your local computer and the A2 Hosting server depends on the local computer's operating system.
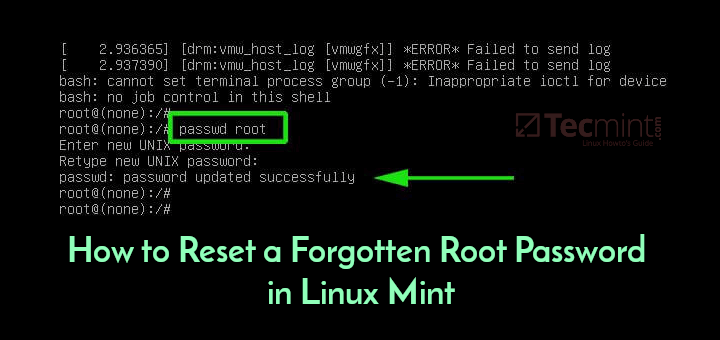
If you know the root password and want to change it, see Section 13.7.1.1, “ALTER USER Statement”, and Section 13.7.1.10, “SET PASSWORD Statement”. If you assigned a root password previously but have forgotten it, you can assign a new password. The following sections provide instructions for Windows and Unix and Unix-like systems, as. I am comprehending what worked in RHEL 7: Terminal 1: sudo service mysql stop sudo mysqldsafe -skip-grant-tables -skip-syslog -skip-networking Terminal 2: mysql -u root UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD('new password') WHERE User='root'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; mysqladmin -u root -p shutdown Note: Once you shutdown mysqladmin, you would be seeing the safe mode exits in Terminal 1.
In this syntax:
First, specify the account name after the CREATE USER keywords. The account name has two parts: username and hostname, separated by the @ sign:
The username is the name of the user. And hostname is the name of the host from which the user connects to the MySQL Server.
The hostname part of the account name is optional. If you omit it, the user can connect from any host.
An account name without a hostname is equivalent to:
If the username and hostname contains special characters such as space or -, you need to quote the username and hostname separately as follows:
Besides the single quote ('), you can use backticks ( `) or double quotation mark ( ').
Second, specify the password for the user after the IDENTIFIED BY keywords.
The IF NOT EXISTS option conditionally create a new user only if it does not exist.
Note that the CREATE USER statement creates a new user without any privileges. To grant privileges to the user, you use the GRANT statement.
MySQL CREATE USER example
First, connect to the MySQL Server using the mysql client tool:
Enter the password for the root account and press Enter:
Second, show users from the current MySQL Server:
Here is the output:
Third, create a new user called bob:
Fourth, show all users again:
The output will be:
The user bob has been created successfully.
Set Root Password Mysql Macro
Fifth, open a second session and log in to the MySQL as bob:
Input the password for bob and press Enter:
Set Root Password Mysql Mac Command
Sixth, show the databases that bob has access:
Here is the list of databases that bob can access:
Seventh, go to the session of the user root and create a new database called bobdb:
Eight, select the databasebobdb:
Ninth, create a new table called lists:
Notice that when you press Enter, instead of showing the mysql> command, the mysql tool shows the -> that accepts new clause of the statement.
Tenth, grant all privileges on the bobdb to bob:
Note that you will learn how to grant privileges to a user in the GRANT tutorial.

Eleventh, go to the bob’s session and show databases:
Set Root Password Mysql Mac Os
Now, bob can see the bobdb:
Twelfth, select the database bobdb:
Thirteenth, show the tables from the bobdb database:
The user bob can see the lists table:
Fourteenth, insert a row into the lists table:
Fifteenth, query data from the lists table:
Set Root Password Mysql Macros
This is the output:
So the user bob can do everything in the bobdb database.
Finally, disconnect from the MySQL Server from both sessions:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MySQL CREATE USER to create a new user in the database server.

- Was this tutorial helpful?
